Cement Ingredients | Components and Composition
Cement is one of the most widely used construction materials in the world. Concrete is used to construct the majority of structures built today in the world. It is one of the main ingredients of concrete. This article will work you through the important facts of cement ingredients that we must be aware of.
What is Cement
Cement is a binder, a chemical compound used in building that hardens, sets, and adheres to other materials to bond them together. Cement is used to produce concrete which is recognized as the second most used resource in the world next to water. Mostly, it is used to make concrete, mortar, grout, etc.
In most cases, cement is used to bond sand and coarse aggregate, not on its own. Mortar for masonry is made from cement mixed with fine aggregate, and concrete is made from cement combined with sand and coarse aggregate.
How Cement is Made
Calcium, silica, aluminum, iron, and other components are combined chemically under close observation and monitoring to create cement.
Limestone, shells, and chalk or marl coupled with shale, clay, slate, blast furnace slag, silica sand, and iron ore are typical ingredients used to make cement.
When heated to high temperatures, these materials combine to form a rock-like substance that is then pulverized into the fine powder that is known as cement.
Cement Ingredients
The Portland Cement ingredient can be classified under two main themes.
- Based on the chemicals available in the cement
- Based on the chemical combination in the cement
Cement Ingredients as per Available Chemicals
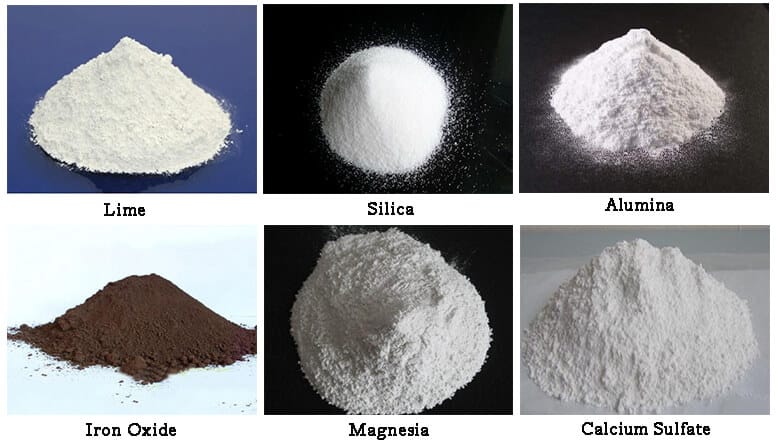
The main chemical available in cement is Calcium Oxide, Silicon Dioxide, Aluminum Oxide, and Iron Oxide. In addition, chemicals such as Magnesium Oxide, Calcium Sulfate, Sulfur, and Alkalis can be identified. The following table indicates their approximate distribution of them.
| Chemical Compound | Formular | Shorter Form | Approx. Percentage |
| Lime – Calcium Oxide | CaO | C | 60 – 65 % |
| Silica – Silicon dioxide | SiO2 | S | 17 – 25 % |
| Alumina – Aluminum Oxide | Al2O3 | A | 3 – 8 % |
| Iron Oxide | Fe2O3 | F | 0.5 – 6 % |
| Magnesia | MgO | 0.1 – 3 % | |
| Calcium Sulfate | CaSO4 | 1 – 3 % | |
| Sulfur | SO3 | 1 – 3 % | |
| Alkalis | 0.1 – 1 % |
Let’s now briefly discuss each type of chemical.
Lime
Lime is known as Calcium Oxide (CaO). As indicated in the above table, it is taking the higher percentage which is 60 – 65 % of the cement and is the major comportment among the Portland cement ingredients. The lime can be obtained from limestone, chalk, and shales. etc.
Lime is important in the strength development of concrete. It shall be maintained at the optimum level. Less content of lime reduces the strength of the concrete and also the setting time of the concrete.
Silica
Silica is also known as Silicon Dioxide (SiO2). It has a low amount (17 – 25 %) when compared to lime. The silica can be obtained from sand, argillaceous rock, etc.
Silica also contributes to the strength of the concrete. Therefore, its compositions shall be controlled correctly as the increase in the connection of Silicon Dioxide will increase the strength and at the same time, it increases the setting time of the concrete as well.
Alumina
Alumina is denoted as Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3). It can be obtained from bauxite, clay containing alumina, etc. Further, it represents the third large amount (3 – 8 %) in cement.
Alumina affects the quick setting of the concrete and also it affects in reducing the clinker temperature leading to produce weak cement.
Iron Oxide
It is known as Fe2O3. and it takes about 0.5 – 6 % of the cement.
Iron Oxide influence the color of the cement. The compound Tricalcium Aluminon Ferrite (4CaO.Al2O3Fe2O3 = C4AF) made by combining lime, alumina, and Iron Oxide, has an impact on the hardiness and strength of concrete.
Cement Ingredients as per Chemical Compositions
The cement’s chemical and physical properties are mostly discussed referring to the variation of percentages of its chemical compositions. The four main chemical compositions of cement are C3S, C2S, C3A, and C4AF.
The following table indicates the names and chemicals included for each composition.
| Compound Name | Formular | Short Name |
| Tricalcium Silicate | 3CaO · SiO2 | C3S |
| Dicalcium Silicate | 2CaO · SiO2 | C2S |
| Tricalcium Aluminate | 3CaO · Al2O3 | C3A |
| Tetra-calcium Aluminoferrite | 4CaO · Al2O3Fe2O3 | C4AF |
In addition to the above, there are other components such as Sodium Dioxide (Na2O), Potassium Dioxide (K2O) and Gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O) used as cement ingredients.
The following table indicates the compound compositions of different types of cement categories as specified according to the ASTM standards. These percentages would change depending on the concrete mix design.
| Cement Type | Use of Cement | C3S | C2S | C3A | C4AF | CS̄2 |
| I | General purpose | 55 | 17 | 10 | 7 | 6 |
| II | Moderate sulfate resistant | 55 | 20 | 6 | 10 | 5 |
| III | High early strength | 55 | 17 | 9 | 8 | 7 |
| IV | Low heat of hydration | 35 | 40 | 4 | 12 | 4 |
| V | Sulfate resistant | 55 | 20 | 4 | 12 | 4 |
C3S – Tricalcium Silicate
It contributes to the early strength of the concrete. It would be around the first week after pouring concrete.
C2S – Dicalcium Silicate
It contributes to the strength development after the C3S
C3A – Tricalcium Aluminate
It contributes to the highest heat of hydration and C3S, C4AF, and C2S have heat generation in descending order.
In conclusion, different cement ingredients would vary depending on the type of concrete to be produced and the type of cement that need to be produced. As discussed above, the variation could be done as per the particular mix design and based on the parameters such as water-cement ratio, expected strength of concrete, based on heat generated during the hydration process, rate of strength gain, etc.