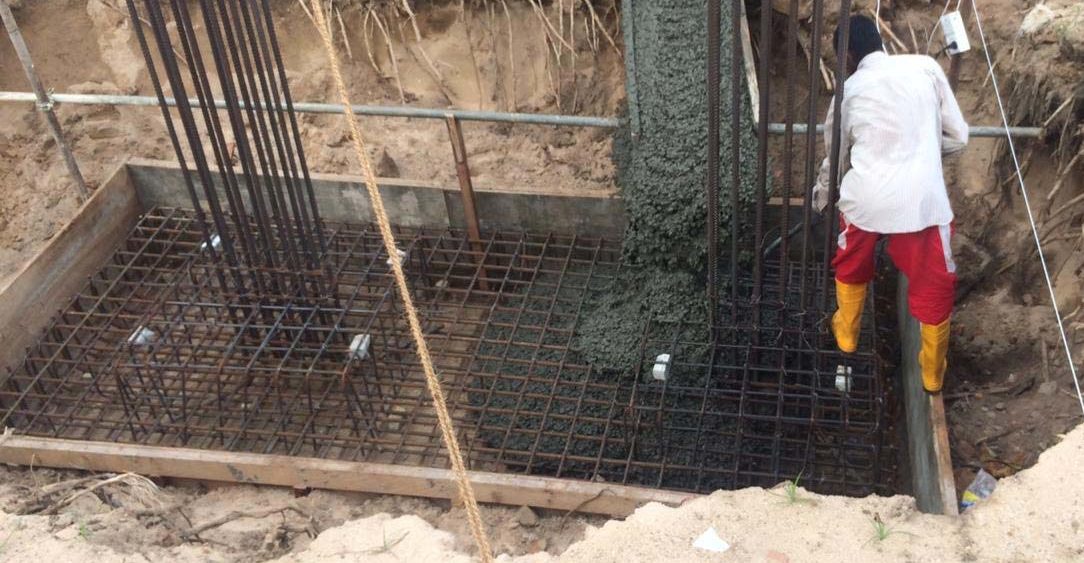
Combined Footing types and design considerations
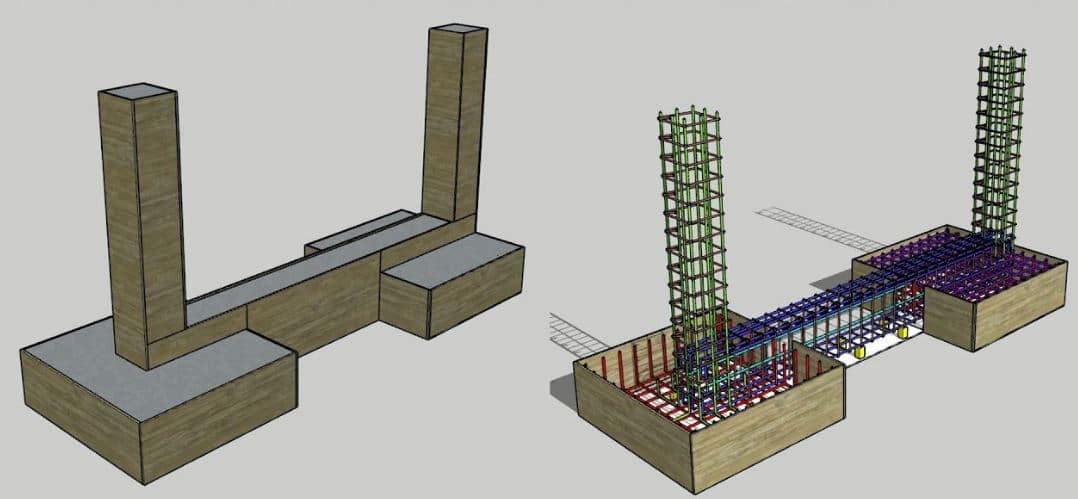
A combined footing is a type of foundation constructed combining two columns. When there are more than two columns, that foundation is called the strip footing.
A combined footing is constructed when the isolated footing can not take bear the applied load along or when there are two columns closed by.
What is a Combined Footing
It is a type of spread footing constructed by combining two columns. The combination of the column may be done as discussed above. The following reasons can be highlighted for the construction of combined foundations.
- The increase in the column axial load resulted in increasing the area of pad footings. When the pressure bulb of each footing is overlapping, there will be a high-stress zone in the soil which could lead to shallow foundation failure. In these situations, we combined the foundation to make a single footing.
- When there are columns a the boundary, we combine the foundation with the inner column.
- An increase in the axial load and reduction in the soil bearing capacity, increase the foundation area. This will also be a reason to combine the foundation.
Types of Combined Footing
- Rectangular Combined footings
- Trapezoidal Combined Footings
- Other shaped footings
- Strap Footing
- Raft Footings
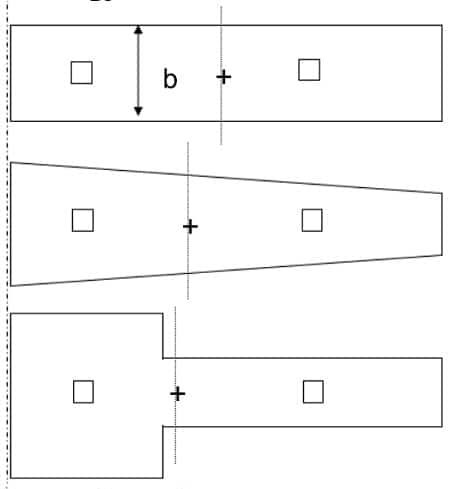
Rectangular Combined Footing
As the name implies, it’s rectangular in shape and it is the most commonly constructed type of foundation.
The design and construction of these types of footings are very easy when compared to the other irregular shapes. The length of the footing and reinforcement is not varied.
The columns of these types of footing may be at the middle of one column may be at the edge of the footing. When there are boundary walls, we cannot continue the foundation to the other land. Therefore, we have to construct a column at the edge of the footing.
Reinforcement detailing is also simple. There are two reinforcement nets (top net and bottom net) for these types of footings.
Trapezoidal Combined Footings
The shape of the footing maybe by the design requirement or as per the limitation of space for the foundation. These types of foundations are not that popular in construction due to the construction deficits.
The varying width of the footing makes the construction more difficult. Lenght of all the reinforcements placed in the shorter direction is varying.
Trapezoidal shape and varied with reduces the area of the footing when compared to a rectangular footing of the same scale. However, this nature of the footing may not reduce the cost of construction.
Other Shapes of Footings
In addition to the trapezial shape and rectangular shape, there are other shape footings constructed as a combination of two columns. The following figure indicates that type of footing.
In addition, it should be noted that these types are not that common in construction and they are constructed only at special occasions. As indicated in the above figure, based on the requirement of the footing, different shapes of the foundations can be constructed.
Strap Footings
It is known the fact why we construct the strap footings. We need not construct strap footings always. Isolated footing itself can act along and bear the applied loads. But there are limitations in the eccentricity of the footing.
With the increase in the axial load, the pressure at the column increases significantly. It will cause excessive settlement of the foundation and soil bearing failures. Therefore, to balance the pressure under the foundation, we connect the eccentrically load footing with normal column footing.
Raft Foundations
The last version of the combined footing is the raft foundation. As discussed, we may avoid the raft foundations or the mat foundation from the combined foundation list. However, it seems it is worth having not on this type of foundation.
It is a combination of all the columns of the structure. Initially, we try to construct the building on the isolated pad footing. However, the increase in the column axial load increases the area of the footings.
When it reaches 66% of the area of the foundation area is occupied with isolated footings, we have no other option rather select a raft foundation.
The design and construction of raft foundations are not as complicated as deep foundations. However, a computer aid analyst will be required for the design.
The thickness of the raft could remain the same or maybe increase at column locations to enhance the bending and shear capacity. Special attention could be made to the punching shear design as we might need to provide the reinforcements at the shear perimeter or increase the thickness of the raft.
How to Design Combined Footing
In this article, we are concentrating on the design of footing have two columns. Let’s see what are the steps to be followed.
- Calculate the service loads of two columns rested on the footing.
- Calculate the area of the footing from the allowable bearing capacity – should be taken from the soil investigating the report.
Arae of footing = [ Total column service load ] / [ allowable bearing capacity ]
- Select dimensions for the footing based on the calculated values. Initially, we assume the width of footing.
- Now calculate the load center. That is the point at which the resultant force is acting. Since the foundation should be asymmetric about this point, now we can calculate the length of the footing.
- This calculation is a trial process and we may be required to adjust the width and length of the footing in the calculation to reach the suitable value.
- Now calculate the ultimate pressure under the foundation.
- Calculate the bending moment writhing equation along the footing. Find the maximum bending moment and shear forces.
- Design for maximum bending moment and share forces.
- Do the rebar detailing.
The worked example design of combined footing could be referred for further information.
Reinforcement Detailing of Combined Footing
Normally, footing connected with two columns has two nets as there are hogging bending moments.
Shear links are not provided as a practice in these types of foundations. However, if required, we may provide the shear links in the event where it is not possible to increase the thickness of the footing to gain the shear capacity.
When the thickness of the footing increases, we need to provide the side reinforcement to avoid cracking of the footing due to the thermal effects.
Factors to be Consider in Design and Construction
- Area of the Footing: The area of the footing is selected based on the column axial load and allowable bearing capacity of the soil. Since two columns are combined there may be a possibility of increasing the area of footing more than that required result reduction in the pressure under the footing.
We select footing areas based on the allowable bearing capacity for all the footing. If there is significant variation in the area of the footing, it changes the pressure under the footing. Different pressures under the footings cause different settlements in the footing. Therefore, special attention shall be made when selecting an area of the footing especially when there is low bearing capacity in the soil which is more susceptible to a higher settlement.
- Ground Improvements: It is required to improve the ground as recommended in the geotechnical investigation report to gain the required bearing capacity of the soil. Soil stabilization or ground improvement methods for low-rise structures could be done under the close supervision of the structural engineer.
Sine the structure rested on the ground, it should have the required capacity to carry the load. Any failure of the weak ground improperly improve could cause the failure of the structure, failure of foundation, settlement of the foundation, etc.
- Consolidation Settlement: It is a long-lasting issue if we do not identify at the initial stage of the project before the design of the foundations. Since the structure contain different type of foundations such as combined footing and isolated footing higher attention shall be made to the soil type.
The necessary measure shall be taken to avoid the settlement of the foundation after the construction. If this is not addressed at the initial stage, there will be many issues that could be difficult the solve. For example, settlement of the foundation could cause cracks in the brick walls. Continuation of the settlement for a longer duration, repairing of cracks will not solve the issue. Cracks could reappear with further settlement in the foundations.
Therefore, as suggested in the article soil types, the necessary measures shall be taken at the initial stage of the design and construction.
Related Articles
- Spread Footing
- Shallow Foundations
- Pier Foundation
- Footing Foundations
- Deep Foundations
- Foundation Failure
- Underpinning
- Eccentrically Loaded Foundations
- Shallow Foundation Failure
- Pile Raft Foundations
- Mat Foundation
- Pile Foundation
- Driven Pile Foundations
- Pile foundations
- Uplift Pressure on Foundations
- How to Determine Foundation Type
- Excavation for Foundation
- Foundation Waterproofing
- Settlement of Shallow Foundations
- Slab Foundations