Vibration of Concrete [methods and correct procedure]
The vibration of concrete is not must always. There are other types of concrete that do not require vibration. However, most of the time, we do vibrate concrete to achieve the required compaction.
When concreting piles, larger raft foundations, underwater construction, etc. are done it is very difficult to vibrate the concrete for getting adequate compaction. In those situations, we use self-compacting concrete where it compacted its self.
Why Vibration of Concrete Required
Except for the self-compacting concrete, all the other types of concrete are normally vibrated by suitable means for consolidation. The followings are the key factors to consider important for having adequate vibration of concrete.
- To reduce the air contained in the concrete. Generally, 5%-8% of voids from total volume contains in the concrete mix. With the vibration, it reduces significantly.
- To consolidate concrete adequately.
- To avoid segregation
- To avoid bleeding
Concrete Vibration Methods
There are about five methods used for consolidating the concrete.
- Form Vibration
As the name implies, the vibration of the formwork is done in this method. This method is used when the other methods are not applicable. Vibrators are fixed into the formwork of the concrete.
Special attention shall be made to the adequacy of the vibration and the spacing of the vibrators to be finalized according. Special vibrators could be used on the following occasions.
- Precast element concreting
- Tunnel Concreting
- In larger concretes where applicable, etc.
- Surface Vibrators
The vibration of the concrete is done through the concrete surface.
This method of vibration is not that effective for thicker concrete pours. The effective depth of the surface vibration of concrete is about 150mm-250mm.
The main disadvantage of these types of vibrators is the limited depth that the concrete will consolidate adequately. Further, there should be adequate density or hardness in the concrete surface to do the vibration.
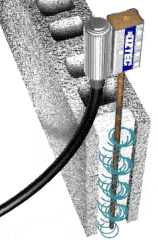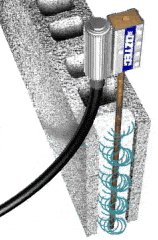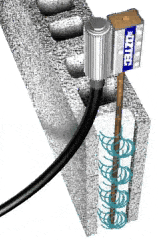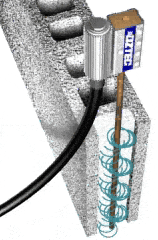
- Internal Concrete Vibrators
The most popular method used for the vibration of concrete.
It is quite simple to use when compared to the other method. The porker vibrator is widely used in construction to consolidate the concrete.
- Rebar Shaker
These types of equipment are used on special occasions as indicated in the following figure.
The vibration of concrete can be done by vibrating the reinforcements. However, this method can not be applied for large pour concretes.
- Concrete Vibrating Table
This is a kind of table used to vibrate the concrete. This is more suitable for smaller concrete. Vibrating tables are used in precast concrete construction.
Best Practices in Concrete Vibration
- It is observed that the concrete is mostly under or improperly vibrated. The concrete could be vibrated about 10s-15s. The vibration time depends on the workability of the concrete. Therefore, the skill of the operator is very important.
- Overlap the previous circle with the new circle every time. In addition, the layers shall also vibrate manner that they are overlapped. The porker vibrator shall at least be inserted 150mm into the previous layer.
- Vibration could be stoped when the entrapped air no longer escaped and the surface is leveled.
- Puling out the porker vibrator could be done not more than 75mm per second. The ideal speed of pulling out the porker vibrator is 25mm per second.
- The vibrator shall not be used to move the concrete to the correct place.
Consequences of Improper Vibration of Concrete
Most issues recorded due to the inadequate concrete consolidation resulting in the improper vibration can be listed as follows.
- Having entrapped air in the concrete increase the voids. It reduced the density of the concrete. It increases the porosity of the concrete.
- As a result, concrete permeability increases. It could affect the durability of concrete. In addition, it could lead to the corrosion of reinforcement.
- Further, high porous concrete could be carbonated, and as a result reinforcement corrosion could be an issue.
- Higher voids in the concrete make lesser the strength of the concrete.
- Formation of the Honeycombs especially in areas with reinforcement conjectures
- Sand streaking caused by the heavy bleeding and mortar loss
- The appearance of Placement Lines
- Cold Joints in the concrete
- Subsidence Cracking
Consequences of Over Vibration
- Segregation of concrete
- Sand Streaks
- Loss of entrained air in air-entrain concrete
- Excessive form deflection
- Excessive form deformations
- Formwork failures
Factors Affecting Compaction of Concrete
- Mix proportions
- Workability of concrete
- Inadequate vibration
- Use of correct mode of vibration.