Cement Waterproofing
Cement waterproofing is quite common in construction in protecting structures against water leakages.
As we all know concrete get cracked due to various reasons. When the crack width is greater than 0.2mm, there are possibilities of leaking the water through the concrete.
Therefore, when a water-retaining structure is built, it is required to protect the structure against leaking water from the structure.
Initially, let’s discuss the main types of waterproofing.
- Cementitious waterproofing
- Torch-on Membrane (Bituminus type)
- Crystalline waterproofing
In this article, we are discussing cement waterproofing. Let’s what is cementitious waterproofing, why we need it, etc.
What is Cement Waterproofing
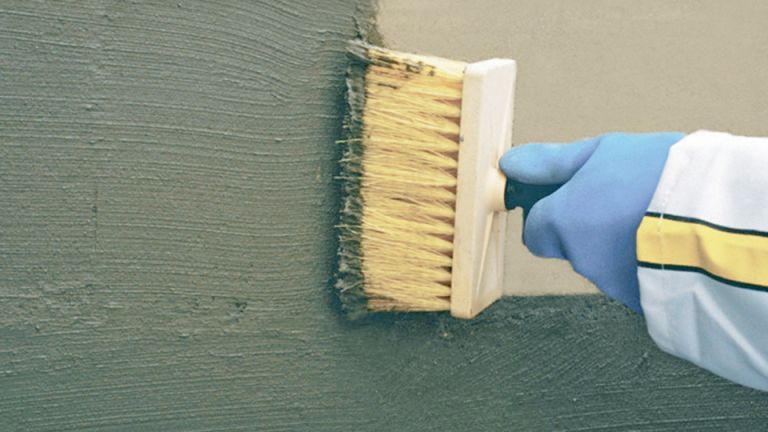
As the name implies, cement waterproofing is a cement-based product used to protect structures. When mixed and applied, it acts as a membrane and avoids the movement of water.
It should have the following properties.
- Freeze/thaw resistance
- Good adhesion
- Good abrasion resistance
- Low absorption to the concrete.
Why do we need Cementitious Waterproofing ?
Cement waterproofing is required to protect the structure against damping and to avoid water leaks through the cracks.
Further, they are used in water retaining structures to bear a certain amount of pressure applied due to the water pressure whether there are cracks in the wall.
What are the Advantages of Cementitious Waterproofing
- Easy to use and mixing
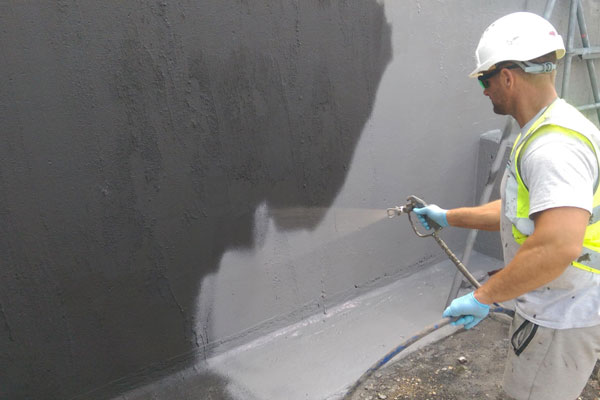
- The application can be done manually or can be used as a spray
- Comparatively, low cost when compared with other types
- Weather resistance – most of them can be used in exposed conditions
- Non-toxic
There are different types of cement waterproofing with different properties. Technological development has made this product more useful in the construction industry.
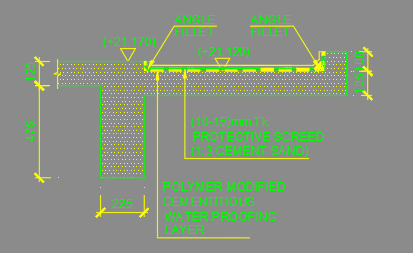
Cement waterproofing is also called polymer modified cementitious waterproofing.
Application and Testing
- After cleaning, the surface is examined. Check the irregularities in the surface. They shall be filled with mortar or cement sand mix.
- Angle fillet shall be placed at the corner to avoid sharp bend. If cement waterproofing is applied at corners without the angle fillet, it could lead to bulging, and as a result, waterproofing may crack or may become less durable.
- Waterproofing shall be applied in two directions. Once applied in one direction, let it dry. After a come time, the second layer shall be applied in a perpendicular direction.
- Let the waterproofing dry.
- Then pond test shall be done. Testing shall be as per the project specification or as directed by the engineer.
- After completing the pond test, a protective screed shall be laid. The minimum thickness of the protective screed could be 10-15mm cement/sand layer.
The following figure indicates typical waterproofing detail.
The following articles could be reffed for further information on waterproofing types and details.