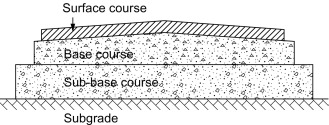
Understanding the Subgrade: Component of Construction
In the world of construction, there are numerous elements that come together to create a solid and reliable structure. Among these, the subgrade is a foundational component that plays a pivotal role in ensuring the durability and stability of roads, buildings, and various infrastructure projects. In this article, we will delve deep into the concept of the subgrade, exploring its importance, characteristics, and the key factors that influence its performance.
What Is a Subgrade
The subgrade refers to the natural soil or aggregate layer located beneath the surface of a road, pavement, or building foundation.
It serves as the primary support for the overlying structure and plays a crucial role in distributing the loads imposed on it.
Requirement of Subgrade in Construction
The subgrade acts as a foundation for the entire construction project, bearing the weight of the structure and any applied loads. Its key roles include:
- Load Distribution
The subgrade evenly distributes the weight of the structure and any traffic loads, preventing uneven settlement and maintaining the integrity of the construction.
In road constructing preparing a quality subgrade is a challenge when the ground conditions are weak. In such situations, ground improvement methods are done.
- Drainage
Proper subgrade preparation ensures efficient drainage, preventing water accumulation that can weaken the structure over time.
Characteristics of a Strong Subgrade
To ensure the longevity and stability of a construction project, the subgrade must possess certain characteristics:
- Compaction
A well-compacted subgrade is essential to prevent settling and shifting of the structure. Proper compaction reduces the risk of uneven settlement, which can lead to structural issues.
- Stability
The subgrade should be stable and able to withstand both static and dynamic loads without significant deformation or shifting.
Preparing the Subgrade
The process of preparing the subgrade involves several crucial steps:
- Excavation
The first step is excavation, where the existing soil is removed to the required depth, ensuring a level and uniform surface.
- Compaction
After excavation, the subgrade is thoroughly compacted to achieve the desired density. This is typically done using heavy machinery to ensure uniform compaction.
In conclusion, the subgrade is an integral component of any construction project, serving as the foundation upon which the entire structure rests. Understanding its importance, characteristics, and the factors that influence its performance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and reliability of any construction endeavor.
FAQs
1. What is the primary function of the subgrade in construction?
The primary function of the subgrade is to provide a stable foundation that evenly distributes the weight of the structure and any applied loads, ensuring the construction’s durability.
2. Why is proper compaction of the subgrade essential?
Proper compaction is essential to prevent settling and shifting of the structure, reducing the risk of structural issues and uneven settlement.
3. How does soil type impact subgrade preparation?
The type of soil at the construction site influences the subgrade’s characteristics and may require different preparation methods, depending on whether it is cohesive (e.g., clay) or granular (e.g., sand) soil.
4. What role does climate play in subgrade performance?
Environmental factors like rainfall and temperature fluctuations can affect the stability and moisture content of the subgrade, impacting its performance over time.
5. Where can I access further resources on subgrades in construction?
For more information and resources related to subgrades in construction, you can visit.