Importance of Subbase in Construction
When embarking on any construction project, whether it’s building a towering skyscraper, a sprawling highway, or even a simple home renovation, the term “subbase” often arises. But what exactly is a subbase, and why is it crucial in construction? In this article, we’ll delve deep into the world of subbases, exploring their significance, types, and the role they play in ensuring the longevity and stability of structures.
What is a Subbase?
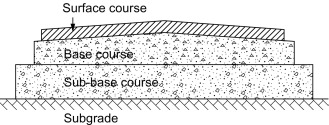
A subbase, in construction terms, is the layer of material placed directly beneath the base or pavement of a structure.
It serves as a critical component that supports the weight of the overlying construction and helps distribute the load evenly across the underlying soil or substrate.
Essentially, the it acts as a foundation for the foundation, making it a fundamental element of any construction project.
Types of Subbases
Subbases come in various forms, each tailored to specific construction needs. Here are some common types:
- Aggregate Subbase
Aggregate subbases are composed of crushed stone, gravel, or sand. They are often used in road construction and act as a stable layer that can withstand heavy traffic loads.
- Asphalt Subbase
Asphalt subbases consist of a layer of asphalt material placed beneath the pavement. They provide excellent durability and resistance to moisture, making them ideal for road projects.
- Concrete Subbase
Concrete subbases are made from a mixture of cement, sand, and aggregate. They are commonly used in building foundations, ensuring stability and preventing settling.
- Soil Subbase
Soil subbases use the natural soil on-site to create a foundation. This type requires careful compaction and preparation to ensure adequate support. This is more common in road construction.
Role of Subbases in Construction
Now, let’s looks at the facts that what its role in structure.
- Load Distribution
One of the primary functions of a subbase is to evenly distribute the weight of the structure above it. This prevents excessive stress on specific areas, reducing the risk of cracks or settling.
- Moisture Control
Subbases help manage moisture by providing drainage for excess water. This prevents water from accumulating beneath the structure, which can lead to erosion and instability.
- Surface Protection
Subbases act as a barrier, protecting the underlying soil from the weight and potential damage caused by construction activities. This ensures the longevity of the structure.
- Stability Enhancement
By offering a stable surface for construction, subbases enhance the overall stability of the project. This is especially crucial for structures like bridges and highways.
In summary, the role of subbases in construction cannot be overstated. These foundational layers provide stability, load distribution, and moisture control, ultimately ensuring the structural integrity and longevity of buildings and infrastructure.
So, the next time you embark on a construction project, remember that a solid subbase is the first step towards success.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why is a subbase necessary in construction?
A subbase is essential in construction because it provides stability, load distribution, moisture control, and surface protection for the overlying structure, ensuring its longevity.
2. What are the different types of subbases?
Common types of subbases include aggregate subbases, asphalt subbases, concrete subbases, and soil subbases, each tailored to specific construction needs.
3. How is proper compaction achieved in construction?
Proper compaction in subbase construction is achieved by eliminating air gaps through thorough compaction, creating a solid foundation.
4. Why is moisture control important in subbase construction?
Moisture control in subbase construction prevents water accumulation, which can lead to erosion and instability, ultimately preserving the structure’s integrity.
5. What role does it play in highway construction?
In highway construction, a subbase offers stability and load distribution, ensuring the durability of the road and its ability to withstand heavy traffic loads.